Description
SX1278 LoRa Module Ra- 02 433MHZ Wireless Spread Spectrum Transmission
The long-range wireless transmission LoRa module Ra-02 is based on the SEMTECH SX1278 wireless transceiver. This LoRa module uses advanced LoRa spread spectrum technology to provide a communication range of up to 10,000 meters. It has excellent anti-jamming skills and an air wake-up consumption feature.
The SX1278 LoRa RF module is designed mainly for long-range spread spectrum communication and has low current consumption. It has a high sensitivity of -148 dBm and a power output of +20 dBm.
Compared to traditional modulation technology, LoRa communication modulation technology provides significant advantages in terms of anti-blocking and selection, interference, and power consumption.
Features
- LoRa ™ Spread Spectrum modulation technology
- Constant RF power output at + 20dBm-100mW voltage change
- Half-duplex SPI communication
- Supports FSK, GFSK, MSK, GMSK, LoRa ™ and OOK modulation modes
- Automatic RF signal detection, CAD mode and very high speed AFC
- Packet engine with CRC up to 256 bytes
- Small footprint dual-row stamp-hole patch package
- Shielded housing
- Spring Antenna
Applications:
- Long-range wireless communication module based on LoRa platform
- Uses SPI communication protocol and requires an antenna for proper RF communication
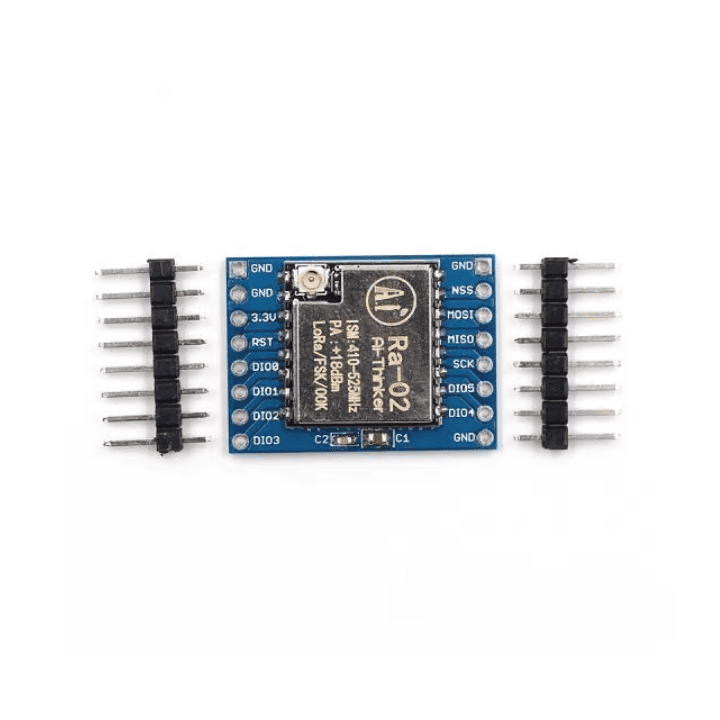
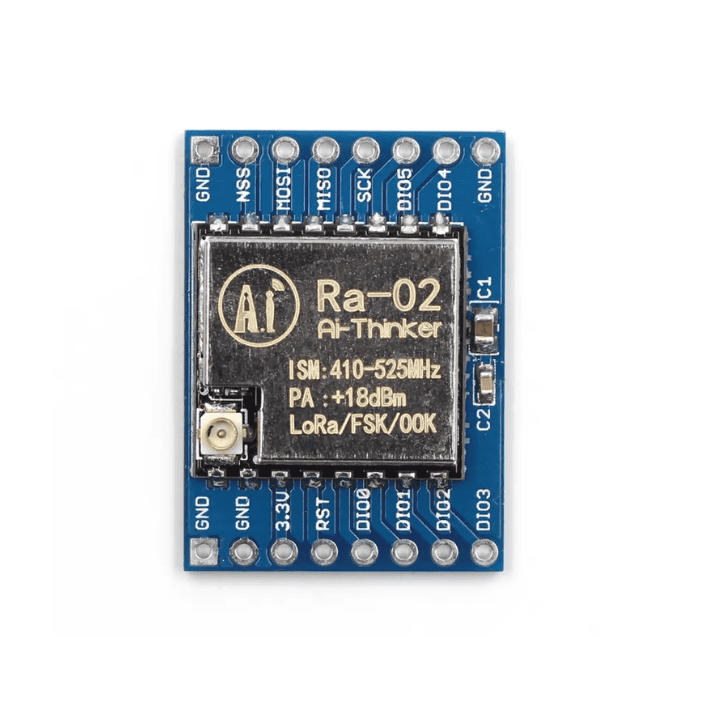
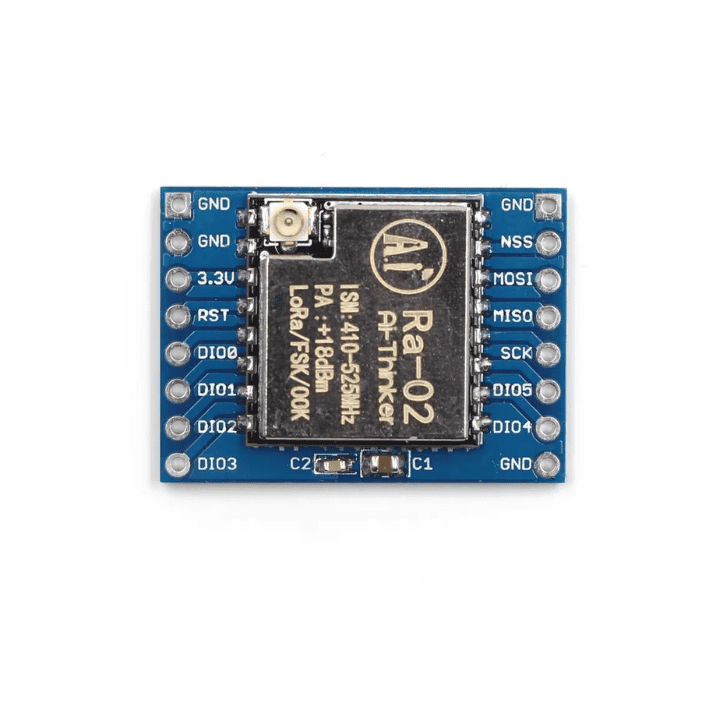
- Operates on 3.3V and has 16 pins (8 on each side)
- Can be interfaced with microcontrollers like Arduino Uno and Nano
- Widely used in Arduino & IoT projects, smart agriculture, smart cities, and industrial automation due to its long-range communication and low power consumption
SX1278 LoRa Module (RA-02 433MHz) – Arduino Connection & Wiring Guide
1. Important Notes Before Wiring
- The SX1278 module operates at 3.3V logic and supply; it is not 5V tolerant. Supplying 5V may damage the module.
- Connect a suitable antenna to the module’s RF output to prevent damage and ensure proper communication.
- Ensure a common ground between Arduino and LoRa module to avoid unreliable communication.
2. Wiring Table (Arduino UNO Example)
| LoRa Module Pin | Arduino UNO Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VCC (3.3V) | 3.3V | Provide stable 3.3V supply. Some boards may require external regulator. |
| GND | GND | Common reference for both devices. |
| NSS / CS | D10 | Chip select for SPI communication. |
| DIO0 | D2 | Interrupt pin for packet-ready signaling. |
| SCK | D13 | SPI clock. |
| MISO | D12 | SPI Master-In-Slave-Out. |
| MOSI | D11 | SPI Master-Out-Slave-In. |
| RST | D9 | Reset pin for LoRa module. |
3. Connection Tips
- Use short wires to reduce noise on SPI lines.
- Keep the LoRa module away from large metal objects or other RF modules to reduce interference.
- If using a 5V Arduino, consider a logic-level shifter on SPI lines to protect the module.
- Ensure VCC is supplied by a 3.3V source capable of sufficient current.
4. Arduino IDE Setup & Example Code
- Install the LoRa library by Sandeep Mistry via Arduino Library Manager.
- Use the following basic transmitter code:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <LoRa.h>
int counter = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("LoRa Sender");
if (!LoRa.begin(433E6)) {
Serial.println("Starting LoRa failed!");
while (1);
}
LoRa.setTxPower(20);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Sending packet: ");
Serial.println(counter);
LoRa.beginPacket();
LoRa.print("hello ");
LoRa.print(counter);
LoRa.endPacket();
counter++;
delay(5000);
}
- For the receiver, use
LoRa.begin(433E6)and read incoming packets.
5. Final Checklist
- Antenna connected
- Module VCC = 3.3V and GND connected
- SPI wiring correct (NSS, SCK, MISO, MOSI)
- DIO0 and RST connected
- Logic levels safe or level shifted
- Library installed and example configured for 433MHz
LoRa Module Comparison: SX1278 vs SX1262 vs RFM95
| Feature | SX1278 Module | SX1262 Module | RFM95 Module |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | ~137‑525 MHz (commonly 433/470 MHz) | ~150‑960 MHz (broad frequency support) | Typically 868/915 MHz (depends on variant) |
| Maximum Transmit Power | Up to +20 dBm | Up to +22 dBm | Up to +20 dBm (varies with module) |
| Receiver Sensitivity | Down to ~‑139 dBm | Down to ~‑148 dBm | ~‑148 dBm (depending on version) |
| Power Consumption / Efficiency | Higher RX current, less efficient | Much improved efficiency, lower RX current | Good efficiency, similar to SX127x series |
| Package / Size | Larger 6×6 mm QFN, older design | Smaller 4×4 mm QFN, newer generation | Module size similar to SX127x based modules |
| Ideal Use Case | Cost-sensitive, 433 MHz or legacy 868/915 projects | Battery-powered, long-term deployments, broad frequency support | Strong 868/915 MHz coverage, general purpose LoRa usage |
| Drawbacks | Older generation, less efficient, limited bandwidth | Higher cost, more complex features may be overkill for simple use | May not offer lowest current draw compared to newest chips |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.